Postgresql on AWS
Author : JaNakh Pon , December 11, 2021
Tags
Postgresql on AWS RDS
In this article, we are going to set up PostgresqlDB using AWS RDS and after that we will use DBeaver client to connect to Postgresql.
Requirements
We will need an AWS account and DBeaver client on our OS to continue. So, let's install DBeaver client first:
> yay -Syu dbeaver
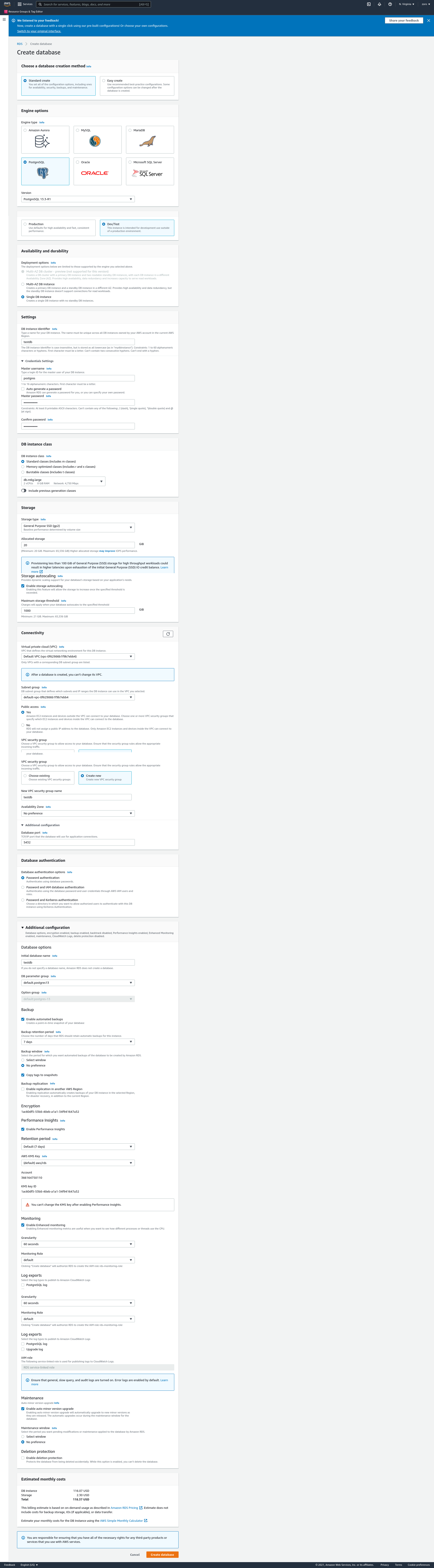
And now we need to sign in to our AWS console and search for RDS and then go to RDS/databases/ and create database. I just want to create just a test database instance so I prefer to follow the default configurations.
However in Connectivity session, I want to give "Public access" and create a new security group so i might be able to configure it however i want without having to alter the existing ones. And in 'Database authentication' session, I prefer to stick to 'Password authentication'.
At the end of the page, you will see a 'Deletion Protection' checkbox and if you happened to select that you won't be able to delete your database. But for me, I want to delete my db instance once after I finished playing it so i will leave it unchecked.
Connecting to postgresql instance via DBeaver
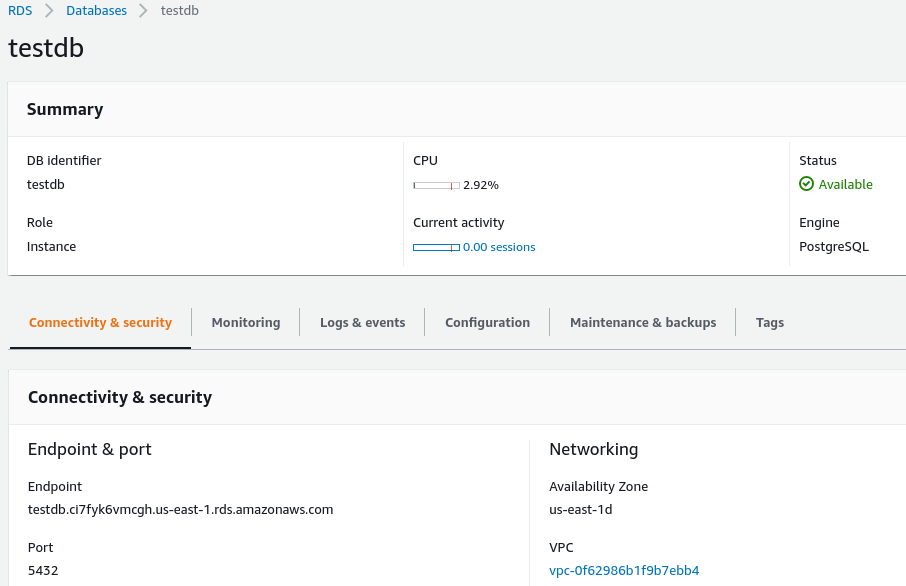
Once our postgresql instance is ready, we need to copy endpoint from our db's connectivity & security session:
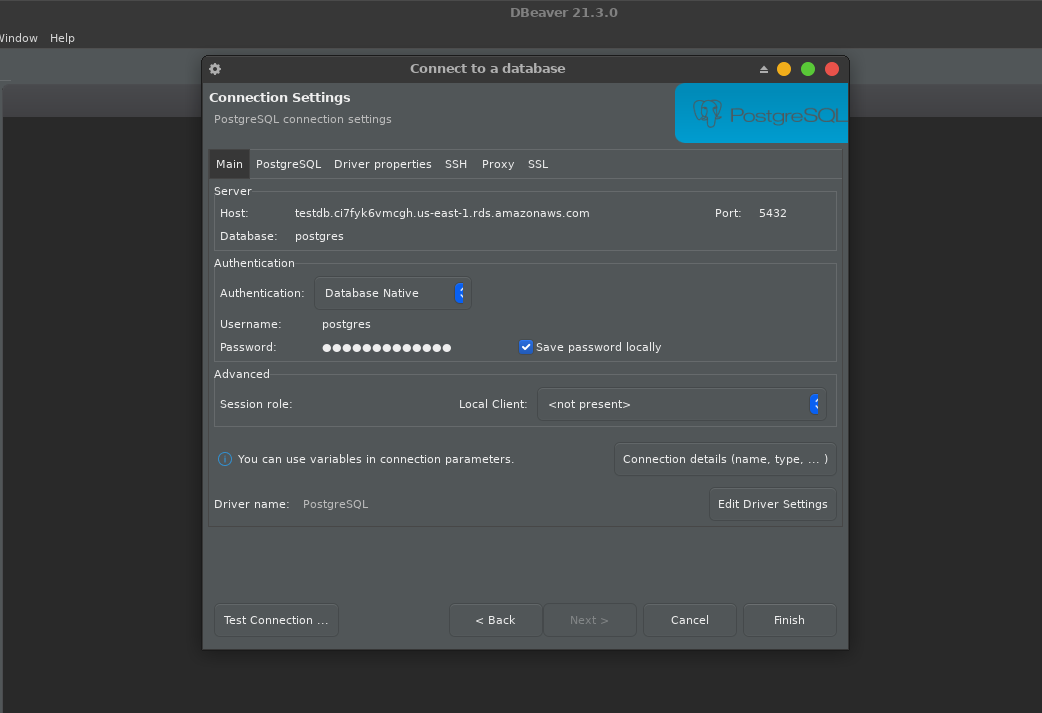
And then open DBeaver and click New Database Connection and put the endpoint alongside username and password:
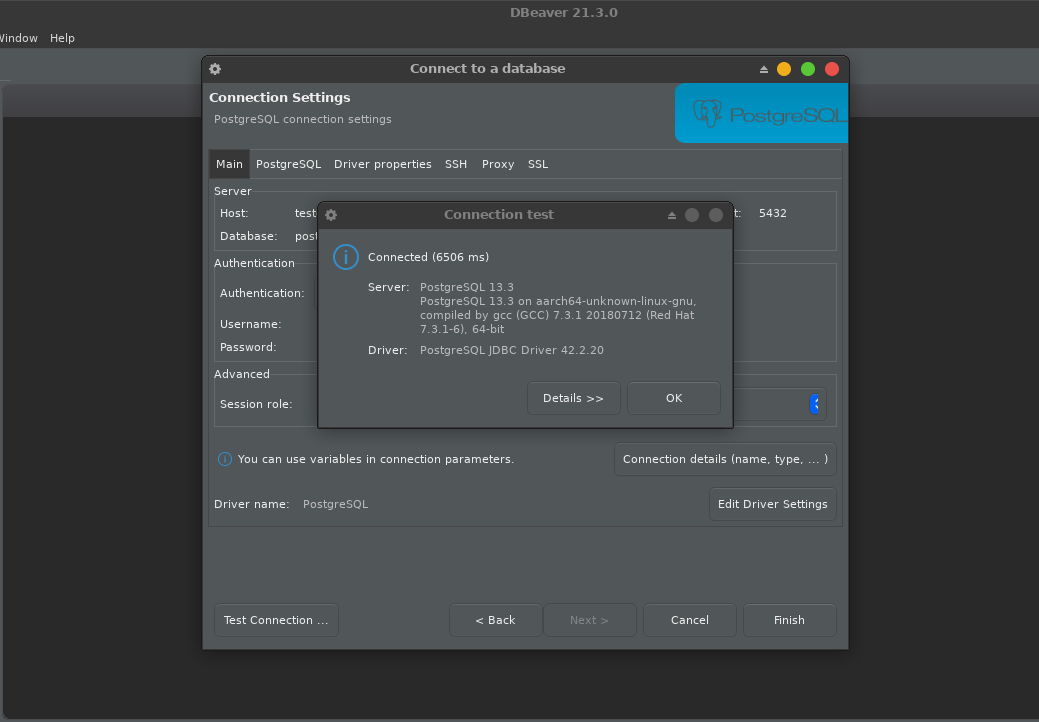
Don't forget to test connection to make sure we put the right credentials:
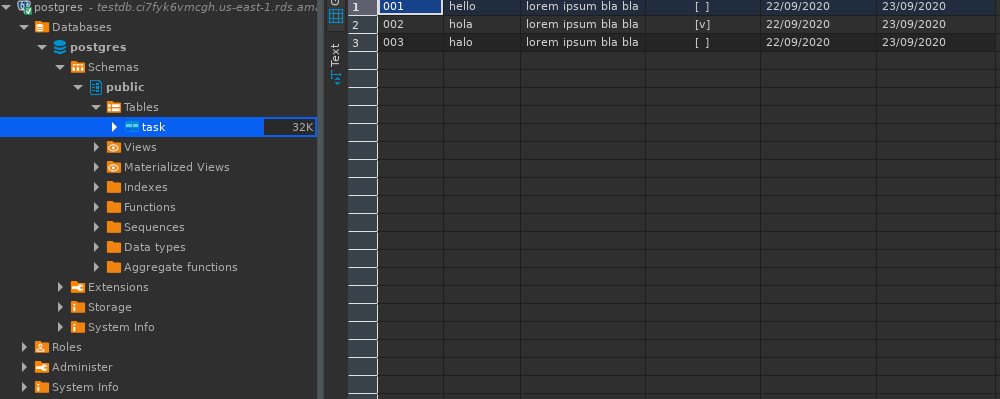
And now, let's create a new table in DBeaver client:
CREATE TABLE task(
id VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(200),
description TEXT,
completed BOOLEAN,
created_at VARCHAR(100),
updated_at VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO task(id, title, description, completed, created_at, updated_at) VALUES ('001', 'hello', 'lorem ipsum bla bla', FALSE, '22/09/2020', '23/09/2020');
INSERT INTO task(id, title, description, completed, created_at, updated_at) VALUES ('002', 'hola', 'lorem ipsum bla bla', TRUE, '22/09/2020', '23/09/2020');
INSERT INTO task(id, title, description, completed, created_at, updated_at) VALUES ('003', 'halo', 'lorem ipsum bla bla', FALSE, '22/09/2020', '23/09/2020');
And we should be able to see the results in DBeaver after refreshing the connection:
Go Back.